health
Refractive Surgery
Summary
Refractive surgery (corrective eye surgery) includes PRK, LASIK, and SMILE procedures, among others.
Market Scope is a research firm that collects data on LASIK procedure rates, and seems to be the primary (if not the only) source for such data. I’ve found an 18-year dataset, 1996-2014 (the last two-years of which were forecast). I’ve contacted Market Scope to inquire if they have long-term forecasts as well.
No US forecasts obtained yet. The best academic paper addressing refractive surgery forecasts (in China) suggests that procedure rates are fairly stable in the US.
Research Excerpts
As of 2011, more than 11 million LASIK procedures had been performed in the United States.
Src:
Dan Lindfield and Tom Poole. 2013 February. “Nd:YAG Treatment of Epithelial Ingrowth.” Cataract & Refractive Surgery Today Europe.
Citing Market Scope.
*
Number of LASIK (laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis) surgeries in the United States from 1996 to 2014 (in 1,000s).
Src:
Market Scope via Statista
(source inferred via other sources quoting the same numbers and attributing to Market Scope. Statista hides their name behind a paywall)
*
In 2012 U.S. procedure volumes were approximately 700,000 procedures per year. The average price point of $1500 per eye in the United States factors to a total U.S. market size of $1.05 Billion / Year.
The model for potential market growth is based on the observation that the laser refractive surgery market in the United States demonstrated saturation at approximately 2.7% penetration, and showed a baseline volume at approximately 1.2% penetration. In this context, market penetration is defined as annual procedure volume compared to the potential candidate pool.
Potential U.S. Candidate Pool = Overall Population (310 Million People)
x Patients in Treatable Age Group of 18 to 45 Years (36.5%)
x Patients with Treatable Refractive Errors (50%)
x Patients with Adequate Disposable Income (50%)
EQUATION 1: General estimate of United States candidate pool for laser refractive surgery. The result calculates to 28.3 million people.
Laser refractive surgery volumes in the United States grew steadily to peak in 2000 at about 1.5 million procedures (eyes). Volume declined during the economic downturn that began in Q4 2001 and rebounded slightly from 2003 through 2007. The U.S. market has not recovered following the macroeconomic downturn of 2008. It stood at approximately 700,000 procedures in 2012. [Citing Market Scope figures given above.]
Src:
Guy Kezirian, et al. 2013. “Forecast of Laser Refractive Surgery in China: 2013-2023.” Northwestern University Kellogg School of Management. Pages i, iii, Figure 1.
Dr. Kezirian (info@surgivision.net) is a board certified and sub-specialty trained ophthalmologist. His company has run several FDA studies for excimer laser approvals. He is an industry consultant in ophthalmology through his company, SurgiVision Consultants.
Email inquiry sent 10/9 seeking recent figures and U.S. forecasts.
*
Ron Krueger, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic in Cleveland, Ohio, discusses his forecast for the future of LASIK procedures.
LASIK will probably be replaced by something else in the next 10 years due to flap complications, biomechanical concerns, dry eye concerns.
SMILE procedure (or something like it) will probably replace it.
Src:
Mark Kontos and Ron Krueger. 2014. “Will LASIK Still Be Kind in 2025?” Aspen 2014. American-European Congress of Ophthalmic Surgery. Eyetube.net.
*
Professional Organizations (inquiries sent 10/13)
American-European Congress of Ophthalmic Surgery
contact form
American Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery
media inquiries form
Outpatient Ophthalmic Surgery Society
Kent L. Jackson, Executive Director, kjackson@ooss.org
American Academy of Ophthalmology
media@aao.org
Update
Trudy Larkins, Executive Direction of AECOS, says:
I think Dave Harmon and Bill Freeman of MarketScope are your best resources.
Since these procedures are elective (i.e. not covered by any type of medical insurance), figures have historically been “best estimates.”
Toric IOLs are extremely popular and perhaps the most widely used. The patient pays out of pocket and the surgeon is able to significantly reduce the amount of pre-op as well as post-op (surgically induced) astigmatism.
We had hoped that having LASIK would become as anticipated as getting braces on your teeth. Unfortunately, this did not happen and some bad PR apparently resonated much more than we anticipated.
I would suggest that you contact someone from the American Refractive Surgery Council. AECOS is an Advisor to this group which is made up of industry as well as refractive surgery physicians. I do know that Richard Lindstrom MD, Eric Donnenfeld MD and Kerry Solomon MD are all very actively involved in this organization and would be great to interview.
CC emailed Dave Harmon at Market Scope directly (10/16/15)
Prosthetic Limbs Forecast to 2050
Summary
In searching for prosthetic device usage rates and forecasts, I’m finding that the most accessible type of data available describes incidence of limb loss and associated prostheses. Data describing usage rates for other types of prostheses and assistive devices has been harder to find (for example, dental prostheses, cochlear implants, artificial heart valves, etc). This summary and set of excerpts focuses on limb loss and associated prostheses.
The CDC, via its National Health Interview Survey, collected data on the number of people using upper and lower limb prostheses. Data was collected in the mid 1990s – I’m not sure if CDC has more recent (or older) figures. (Email inquiry on Oct 6, 2015. No reply as of Oct 8.)
The US Department of Health and Human Services has documented rates of amputation in the US via its Healthcare Cost And Utilization Project (HCUP), although this effort does not document rate of prostheses usage. Estimated rates of prosthesis usage by amputees vary widely.
The National Commission on Orthotic and Prosthetic Education (NCOPE) has published a workforce demand study forecasting prosthesis user figures through 2020. An academic study has forecast amputee figures to 2050. We could apply the usage rate used in the NCOPE study to extrapolate a number of users from that second study.
*
Follow-up Notes
CC emailed CDC. CC emailed reps from SFB’s Devices & Materials Committee and BMES’s Medical Devices Special Interest Group (including someone from FDA).
Donna Lochner (FDA) is not aware of any centralized repositories for overall prosthetics data, but she made a few suggestions by email: check the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) for the Medicare population, and individual registries by product areas (eg: INTERMACS for mechanically-assisted circulatory support devices; the Society for Thoracic Surgeons and the American College of Cardiology for transcatheter heart valves). Lochner thinks the highest volume implants are intraocular lenses, and this might be an area where CMS data would capture the vast majority of the implants.
Emailed William Polglase of CMS for assistance in interpretting data (10/15).
Emailed Medtech Solutions (recommended by BMES) to ask about general tallies.
Research Excerpts
Currently, there are an estimated 1.9 million people living with limb loss in the United States, almost half of whom are non-white. At its peak, an estimated 185,000 amputations occurred in 1996 in the United States.
Amputation rates in the total population (including individuals without diabetes, or with peripheral artery disease alone) are not known and active surveillance efforts do not exist.
Src:
Limb Loss Task Force/Amputee Coalition. 2012. “Roadmap for Preventing Limb Loss in America: Recommendations From the 2012 Limb Loss Task Force.”
*
82% [of amputations] are due to Peripheral Vascular Disease and Diabetes. More than 65 percent of amputations are performed on people age 50 and older.
While diseases such as diabetes and peripheral vascular disease are the leading causes of amputation, accidents and war continue to play a major role in driving the limb prosthetics market.
Technological growth and an increasing consumer base of amputees are bolstering the prosthetics market growth, according to an analysis from the business and research consulting firm Frost & Sullivan. The overall prosthetics market in the United States earned revenues of $1.45 billion in 2006 and estimates that number to reach $1.85 billion by 2013. The global dental prosthetics market is estimated to exceed $5 billion. Hip and knee replacements are big drivers of the orthopedic prosthetic market. Over 100,000 cochlea implants are currently in place globally. The limb future prosthetics devices and the accompanying services market are estimated to exceed $5 billion (of which an estimated $3 billion alone is in amputee patient services) in the U.S.
The lack of common standards, a common lexicon and common data collections negatively impact on the ability to assemble precise market data on limb prosthetics. A National Institutes of Health study concluded, “For example, documented rates of prosthesis use vary from 27 to 56 percent for upper-limb amputation (ULA) and from 49 to 95 percent for lower-limb amputation (LLA). A number of studies have attempted to identify variables that explain inconsistent use rates and identify persons less likely to wear and benefit from a prosthesis. Unfortunately, the existing literature is equivocal and limited by a number of factors.”
Research at the Bioengineering Institute of Worcester Polytechnic Institution, University of Utah, University of Washington and the University of Illinois at Chicago are current leaders in osseointegration and limb transplantation research.
Among the sources for this market analysis are:
Walter Reed Army Medical Center
Henry Jackson Foundation
Amputee Coalition of America
O&P Edge
The Press-Enterprise
Frost & Sullivan
Securities and Exchange Commission
Boston Globe
Aetna Insurance
Atlas of Prosthetics
National Institutes of Health
Disabled-World.com
One Source
ArmDynamics.com
some of the above tallies are from:
Persons Living with Limb Loss, 1996
National Health Interview Survey, Vital Statistics Report, Series 10, No. 200.
New Cases of Limb Loss, 1996
Health Care Utilization Project National Inpatient Sample (HCUP-NIS), 1996.
It is estimated that approximately 199,000 persons in the U.S. were using an artificial limb in 1994, with the majority using an artificial leg or foot (173,000).
Datasource: National Center for Health Statistics,
Disability Report. Table 1
EMAILED nhis@cdc.gov TO SEE IF ITS BEEN UPDATED
Src:
Dr. Grant McGimpsey and Terry C. Bradford. “Limb Prosthetics Services and Devices” [White paper]. Bioengineering Institute Center for Neuroprosthetics, Worcester Polytechnic Institution.
*
The total number of persons with an amputation, and those using a prosthesis, is expected to increase by at least 47% by the year 2020.
The projected number of persons with amputations (excluding tips of fingers and toes) is based on rates by age group and sex determined in the 1993 Health Interview Survey. These projections (Table VII) assume that the rates will remain stable through the year 2020. The total number of persons with an amputation is expected to increase by 47% between 1995 and 2020. Of the total number of persons with amputations it is estimated that 75% use a prosthesis. The population using a prosthesis is also anticipated to increase by 47% during this time period. With the advent of improved prosthetic designs and lighter materials it is likely that the rate of use may increase, particularly if third party payers become more aware of the benefits of these products.
Table VII
Projected Number of Persons with Absence of Extremities
(excluding tips of fingers and toes) 2000-2020
Year — Total Number — No. Of Users of Prostheses*
2000 — 1,752,838 — 1,314,629
2005 — 1,904,035 — 1,428,026
2010 — 2,065,993 — 1,549,495
2015 — 2,224,022 — 1,668,017
2020 — 2,382,413 — 1,786,810
*Based on 75% of total numbers of persons with amputations.
Src:
Caroline C. Nielsen. 2002 May. “Issues Affecting The Future Demand For Orthotists And Prosthetists:Update 2002.” National Commission on Orthotic and Prosthetic Education
Citing:
Benson, V and Marano, MA. Current Estimates for the National Health Interview Survey, 1993. National Center for Health Statistics. Vital Health Statistics 10 (190). 1994.
Estimated number of persons with an amputation using a prosthesis (75%) estimated from data in 1) Current Estimates for the National Health Interview Survey, 1993 ; 2) Scremin, A.M. et al. Effect of Age on Progression Through Temporary Prostheses After Below-Knee Amputation. Am. J. of Phys. Med. and Rehab, 1993, and 3)Nielsen, C.C. A Survey of Amputees: Functional Level and Life Satisfaction, Information Needs and the Prosthetist’s Role, JPO, 1991.
NOTE: An updated version of this report was produced for NCOPE in 2015, but it does not provide estimates for the number of prosthesis users. (Instead it calculates the number of O&P doctors in demand.) I’ve written to the author to inquire if that data is available. The updated report is:
Joan E. DaVanzo, Audrey El-Gamil, Steven Heath, et al. 2015. “Projecting the Adequacy of Workforce: Supply to Meet Patient Demand.” National Commission on Orthotic and Prosthetic Education. p.17, Exhibit 5 – 2014 figures. p.19, Exhibit 6 – 2016, 2025 projections.
*
In the year 2005, 1.6 million persons were living with the loss of a limb. It is projected that the number of people living with the loss of a limb will more than double by the year 2050 to 3.6 million.
Table 3
Projected Prevalence of Limb Loss by Etiology and Age (in thousands)
Year — Total
2005 — 1,568
2010 — 1,757
2020 — 2,213
2050 — 3,627
…Most striking, however, are the projected trends for the number of people living with the loss of a limb. This increase is related to the aging of the population and the associated increase in the number of people living with dysvascular conditions, especially diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes in the United States is projected to nearly double by the year 2030 solely because of changes in the demographic composition of the population. Our estimates of limb loss reflect, and indeed magnify, these trends. Even assuming that age-, sex-, and race-specific rates of both diabetes and diabetes-related amputations remain unchanged, the number of people with diabetes who are living with the loss of a limb will nearly triple by the year 2050. Overall, the prevalence of limb loss will more than double from 1.6 to 3.6 million people. Given the increase in the prevalence of obesity and the known relationship between obesity and diabetes, a projected increase in the incidence of amputations secondary to dysvascular conditions is likely.
…A goal of Healthy People 2010 is to reduce the number of lower-extremity amputations in persons with diabetes by 55%, from 4.1 per 1000 to 1.8 per 1000 persons.
Src:
Ziegler-Graham K, MacKenzie EJ, Ephraim PL, et al. 2008. “Estimating the prevalence of limb loss in the United States: 2005 to 2050.” Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 89(3).
*
UPDATE 10/27: INTERMACS confirmed tallies for ventricular assist devices from 2006-2015. They estimate that their figures cover 90-95% of the market.
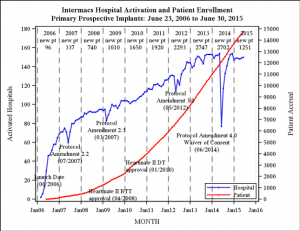
[click for larger]
Annual new patient tallies are at the top of the chart area.
Injuries Data
Current injuries data is collected by two federal agencies, the Centers For Disease Control, and the Bureau for Labor Statistics. The CDCs data describes overall injury rates (fatal and nonfatal) going back to 2002. BLS’s data describes work-related injury and illness rates (fatal and nonfatal) going back to 1992 (only 2003 for nonfatal incidents).
The Pardee Center for International Futures produces the most long-ranging forecasts for injury- and illness-related fatalities that I’ve found so far. (As far as I can tell, their forecasts do not included non-fatal incidents.) I’ve taken samples of their data from the top of the decade through 2050, but annual data are available from 2010 through 2100.
Data from all three sources (CDC, BLS, and Pardee) are aggregated in this Google Spreadsheet:
This graphic from a 2011 Pardee paper shows the general trend in fatalities due to injuries versus disease:

Src: Barry B. Hughes, Randall Kuhn, Cecilia M. Peterson, et al. 2011. “Projections of global health outcomes from 2005 to 2060 using the International Futures integrated forecasting model.” Bulletin of the World Health Organization.
Sick Days and Chronic Illness
I consulted a few different sources of information for illness statistics. The Bureau of Labor Statistics has a very small sample of sick-leave used data (for 2009). Gallup and Healthways also have a small sample of sick-leave data (for 2012). No forecasts are available. Several think tanks are tracking reported rates of chronic illness. A couple forecasts are available. Results are summarized below.
Sick Days
In 2012, researchers from the Bureau of Labor Statistics conducted a one-time tabulation of sick leave provision and usage. The data used were compiled from the 2009 National Compensation Survey, looking only at full-time workers in private industry.
The researchers averaged the amount of sick leave used in each of 6 industry areas (financial activities; information industry; trade, transportation, and utilities; professional and business services; leisure and hospitality; construction). In the first four of those industries, workers used an average of 4 days of sick leave per year. In the last two industries (leisure and hospitality, and construction), workers used an average of 2 days of sick leave per year.
This was a one-time tabulation. Jason Ford says by email that he’s not aware of any forecasts. To his knowledge, additional years of this data are not available.
Src:
Ross O. Barthold, Jason L. Ford. 2012 February 29. “Paid Sick Leave: Prevalence, Provision, and Usage among Full-Time Workers in Private Industry.” Bureau of Labor Statistics.
*
2012 survey data of workers in 14 job categories found that usage of sick days ranged from 6 days per year to 3 days per year. The survey was conducted by Gallup and Healthways as part of Healthways’ annual Well-Being Index report. The survey was administered to 94,000 Americans who work at least 30 hours per week.
Days missed per month
Physicians: .24
Farmers, Foresters, Fishers: .25
Construction or Mining: .28
Installation/Repair: .35
Sales: .35
Managers/Executives: .36
Professionals: .37
Manufacturing/Production: .38
School Teacher: .39
Transportation: .40
Business Owners: .41
Nurses: .43
Clerical or Office Workers: .44
Service Workers: .47
Note: 24/7 Wall St. performed the analysis of data collected by Gallup-Healthways. Emailed Healthways (9/25) to see if they’re still collecting this data.
Src:
Michael B. Sauter, Samuel Weigley and Alexander E.M. Hess. 2013 May 9. “Workers Taking the Most Sick Days.” 24/7 Wall St.
Well-Being Index
Gallup and Healthways have compiled their Well-Being Index annually since 2008. It’s a “barometer of Americans’ perceptions of their well-being.” The index is compiled based on survey responses to questions about six areas of life: life evaluation, emotional health, work environment, physical health, healthy behavior, basic access.
Physical Health Index
2008 76.9
2009 76.6
2010 76.9
2011 76.7
2012 77.0
2013 76.4
The Physical Health Index is comprised of questions related to: Body Mass Index, disease burden, sick days, physical pain, daily energy, history of disease, and daily health experiences.
Overall Well-Being Score
2008 66.5
2009 66.3
2010 66.8
2011 66.2
2012 66.7
2013 66.2
Over the six years of our well-being measurement, Americans’ life evaluations have improved, emotional health and healthy behaviors have remained stable, and basic access, physical health, and work environment have declined. While there are dozens of trends that have impacted the national score since 2008, the three most prominent ones are:
* Annual decreases in the rate of those with health insurance;
* Rising rates of obesity;
* Declining work environment scores.
Src:
Gallup-Healthways Well-Being Index. 2014. “State of American Well-Being.”
Chronic Disease Rates
In 2008, The Milken Institute found that one third of Americans reported having at least one of seven common chronic diseases, with a total of 162.2 million cases in 2003. They forecasted a 42% increase in cases of those diseases by 2023, for a total of 230.7 million cases.
Of the seven chronic diseases, pulmonary conditions were the most common, with 49.2 million cases recorded. Next in prevalence were hypertension, with 36.8 million recorded cases, and mental disorders, with 30.3 million; followed by heart disease at 19.2 million; diabetes at 13.7 million; cancer at 10.6 million; and stroke at 2.4 million.
Src:
Ross DeVol, Armen Bedroussian. 2007. “An Unhealthy America: The Economic Burden of Chronic Disease.” Milken Institute.
*
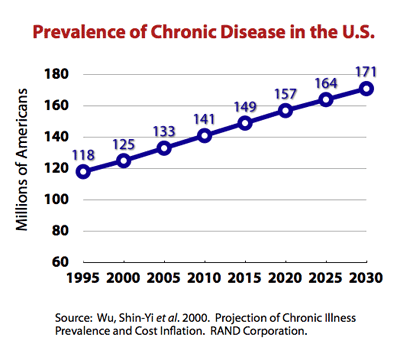
In 2009, almost half of Americans, 145 million people, had at least one chronic condition. This represented an increase of 10 million people over the estimate that was made in 2002 for the year 2009.
The number of people with chronic conditions reached 125 million in 2000, forecast to reach 147 million by 2010 and 157 million by 2020. By 2030 half the population will have one or more chronic conditions.
Src:
2010. “Chronic Care: Making the Case for Ongoing Care.” Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.
*
Prevalence of Chronic Disease in the U.S. Population
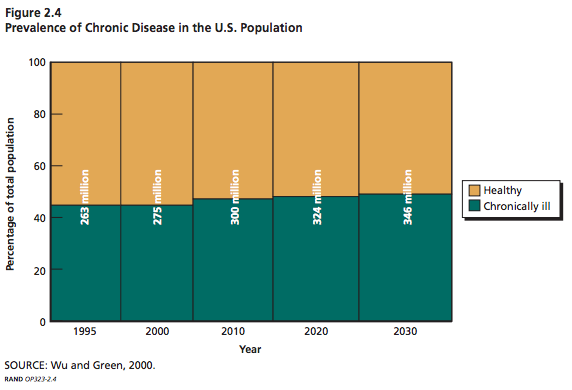
Millions of Americans
Src: Wu, Shin-Yi and Anthony Green. Projection of Chronic Illness Prevalence and Cost Inflation. RAND Corporation; October 2000. (unavailable online)
Cited in:
Soeren Mattke, Lisa Klautzer, Tewodaj Mengistu, et al. 2010. “Health and Well-Being in the Home.” RAND Corporation.
and
The Marshall Protocol Knowledge Base. 2012. “Incidence and Prevalence of Chronic Disease.” Autoimmunity Research Foundation.
Supplement Usage Prevalence
Usage Trends
The CDC tracks U.S. dietary supplement usage (which includes multivitamins and multiminerals) via its National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), which began in the 1970s. In 2011, the CDC said over half of U.S. adults were taking dietary supplements.
Overall usage trend:
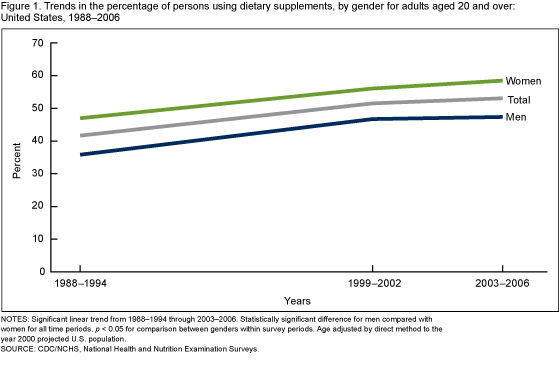
Usage prevalence percentages for adults over 20:
| Year | Men | Women |
| 1971-1975 | 28% | 38% |
| 1976-1980 | 32% | 43% |
| 1988-1994 | 35% | 44% |
| 1999-2000 | 47% | 56% |
| 2003-2006 | 47% | 59% |
Vitamin D use by age group and gender:
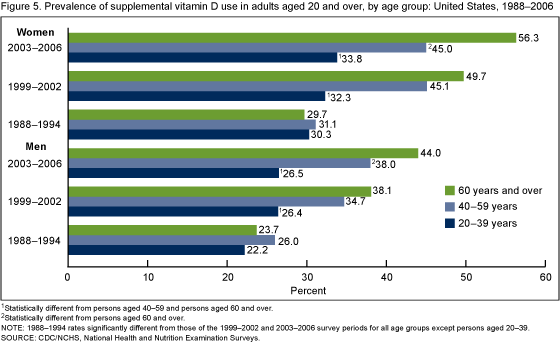
Srcs:
Gahche J, Bailey R, Burt V, et al. 2011. “Dietary Supplement Use Among U.S. Adults Has Increased Since NHANES III (1988–1994).” NCHS data brief, no 61. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics.
Madison Park. 2011 April 13. “Half of Americans Use Supplements.” CNN.
Market Research
Euromonitor tracks the vitamins and dietary supplements (VDS) market. In 2013, they estimated that the market would grow at a CAGR of 4% between 2013 and 2018 to reach $112 billion in 2018.
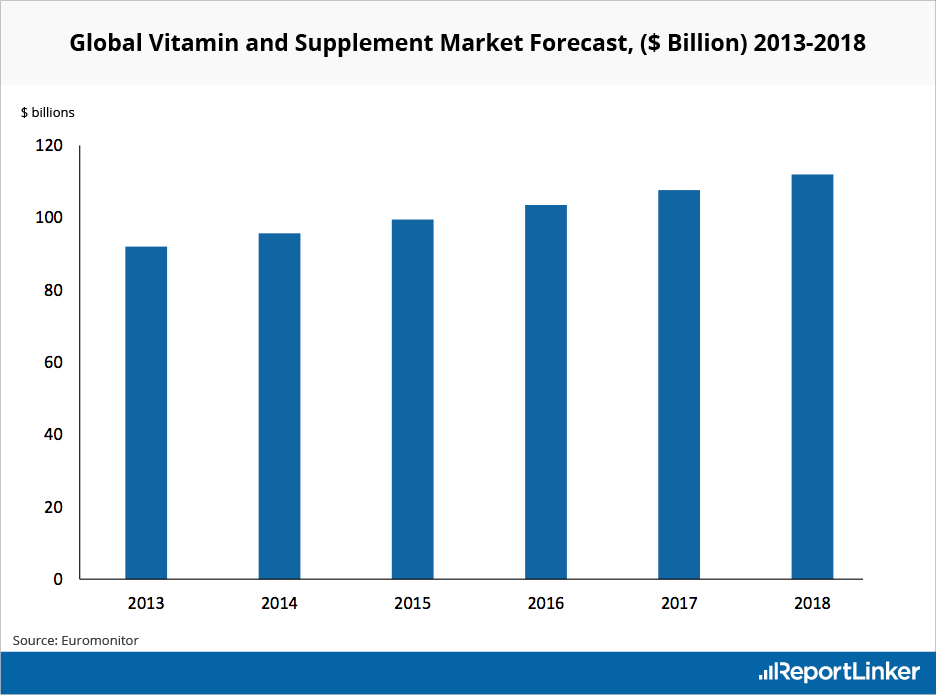
Src:
Euromonitor (via Reportlinker). 2013. “Global Vitamin and Supplement Industry Overview.”
Per Capita Rx Usage
Current data
Evaluate and IMS Health both track current and recent rates of drug prescription per capita.
From Evaluate:
2011: 10
2013: 9
src: 2013. Evaluate. Medical Expenditure Panel Survey. Spreadsheet shared by email, 2015 Sep 10.
From IMS Health:
2010: 11.46
2011: 11.33
2013: 12.2
2014: 2.1% more than 2013
Src (2010, 2011): 2012. IMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics. “The Use of Medicines in the United States: Review of 2011.″
Src (2013): 2014. IMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics. “Medicine use and shifting costs of healthcare: A review of the use of medicines in the United States in 2013.″
Src (2014): 2015. IMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics. “Medicines Use and Spending Shifts: A Review of the Use of Medicines in the U.S. in 2014.″
Michael Kleinrock, of IMS, explains via email that Rx usage rates have been very consistent for a very long time. Their data goes back to the early 90s, but the collection of age-band data is a relatively recent addition. They haven’t yet produced harmonized figures showing all of their historic data.
Forecast data
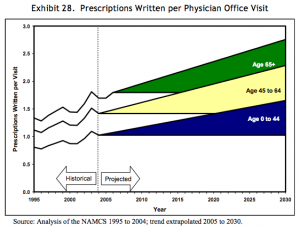
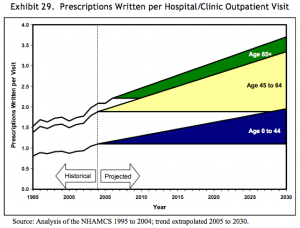
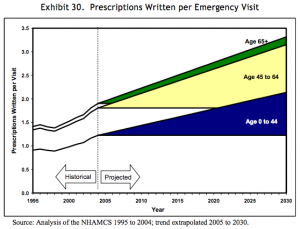
In 2008, a paper published by the Department of Health and Human Services gave forecasts for prescriptions dispensed per visit to the year 2030. Three forecasts were made for prescriptions per physician office visit, per hospital/clinic outpatient visit, and per emergency visit. The forecasts are divided into age bands for patients aged 0-44, 45 to 64, and 65 years and older. The forecasts are all based on analysis of the CDC’s National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS) from 1995 to 2004, with trend extrapolation from 2005 to 2030.
Src: 2008. Department of Health and Human Services. “The Adequacy of Pharmacist Supply: 2004 to 2030.” Exhibits 28-30, pp 31, 32.
Dental Braces Usage
Statistics describing dental services and usage rates are collected as part of the previously cited Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS topics: Dental Visits/Use/Events and Expenditures). Unfortunately, the publications that summarize this data often do not include procedure-level details, but instead focus on dental expenditure on the whole as a percentage of health spending.
One exception I’ve found is a paper from 2007 comparing detailed statistics from 1996 and 2004. Here are relevant excerpts:
The total number of procedures increased from about 496 million in 1996 to about 572 million in 2004.
Distribution of dental procedures1996 2004 Diagnostic 40.2% 42.5% Preventive 29.0% 30.4% Restorative 8.2% 6.9% Prosthetic 7.3% 6.4% Oral surgery 4.1% 3.3% Periodontic 0.9% 0.9% Endodontic 2.1% 1.7% Orthodontic 6.8% 6.9% Other* 1.5% 1.0%
Diagnostic includes exams and x-rays.
Preventative includes cleanings, flouride, sealants and recall visits.
Restorative includes fillings and inlays.
Prosthetic procedures include crowns, bridges, and dentures.
Periodontic procedures include gums.
Endodontic procedures include root canals.
Orthodontic procedures include braces.
Other includes any other dental service not included above.
Src:
Richard J. Manski and Erwin Brown. 2007. “Dental Use, Expenses, Private Dental Coverage, and Changes, 1996 and 2004.” Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.
Co-author Richard Manski (rmanski AT umaryland DOT edu) has written a couple of foreward-looking papers for RAND. I’ve emailed him to ask if he is aware of any ~10-year forecasts for dental braces usage.
EDIT: Manski is unaware of any forecasts.
Dental raw data from the on-going MEPS survey is available here: MEPSnet/HC Trend Query. Raw data for orthodontic visits in 2012 is here, for example: 2012 Full Year Person-Level File. DVGEN12 – # GENERAL DENTIST VISITS 12. Assistance in interpreting the data would be helpful.
Primary Care Office Visits in 2025
“Driven by population growth and aging, the total number of office visits to primary care physicians is projected to increase from 462 million in 2008 to 565 million in 2025. After incorporating insurance expansion, the United States will require nearly 52,000 additional primary care physicians by 2025.”
Src:
Petterson, Stephen M., Winston R. Liaw, Robert L. Phillips, David L. Rabin, David S. Meyers, and Andrew W. Bazemore. 2012. “Projecting US Primary Care Physician Workforce Needs: 2010-2025.” The Annals of Family Medicine 10 (6): 503–9.
The study was based on data from the annual Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS), conducted by the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
In addition to the MEPS data, the CDC also produces annual estimates of physician office visits, as well as hospital visits via it’s National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS) as well as its National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NHAMCS). Tables of recent survey results are available here. We’ve not yet found a forecast for hospital visits, but we’ve aggregated NAMCS and NHAMCS figures going back to 2000 here.
State of the Future Index (28 variables)
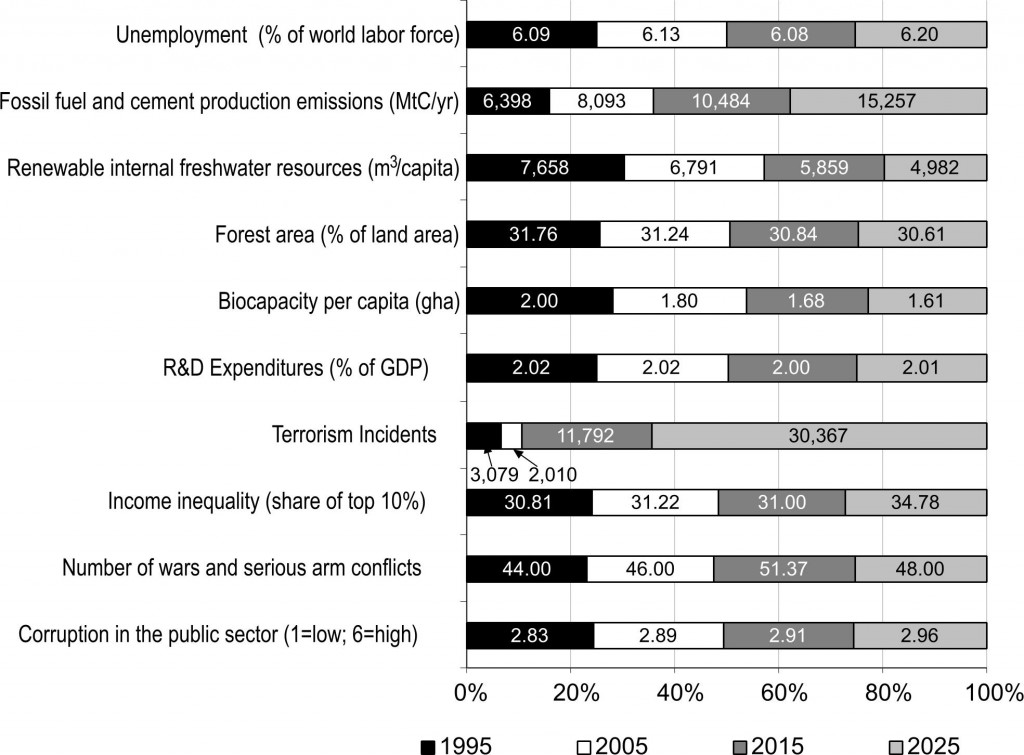
Every year, The Millennium Project (MP) computes a “State of the Future Index” looking 10 years into the future, based on data from the previous 20 or more years. The index calculation is based on values for multiple, individually-forecast key variables (28 in 2015). The index is calculated globally, as well as for individual countries. The overall index is intended to show the direction of things to come.
For our purposes the forecasts for the 28 individual variables are of most interest. MP breaks the variables into two groups: those showing improvement, and those showing decline. The values for the individual variables (previous actual, and forecast) are displayed within the shaded area of the charts.
Areas showing improvement in 2015:
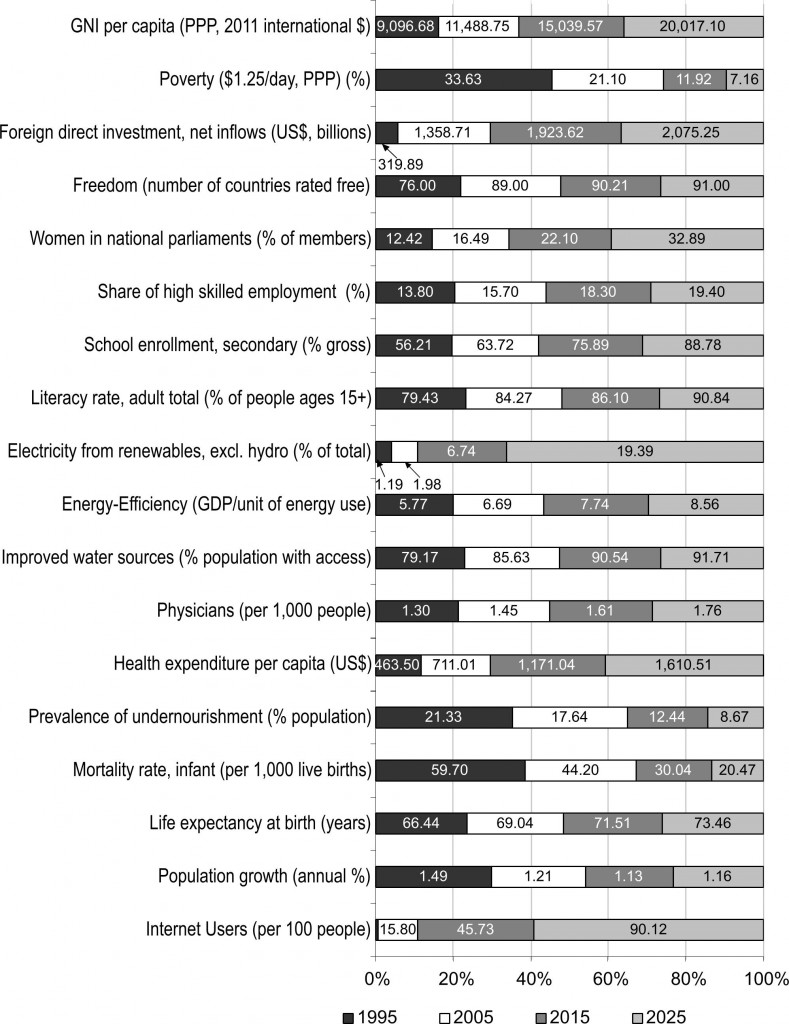
Areas showing decline in 2015:
In 2015, the calculated Index looks like this:
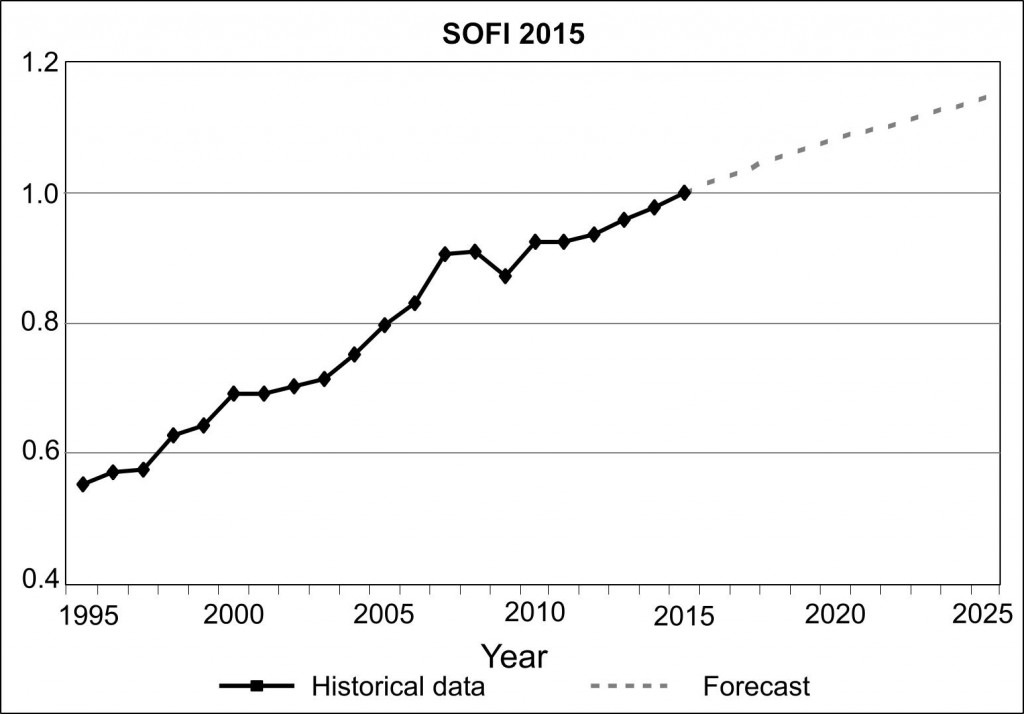
Src: Gordon, Theodore J. 2015. “2015 State of the Future Index.” The Millennium Project.
Charts for each indicator, and a brief indication of the source for the data are in this PDF.
The Millennium Project is an independent non-profit global participatory futures research think tank of futurists, scholars, business planners, and policy makers who work for international organizations, governments, corporations, NGOs, and universities. Their annual report collects and assesses judgments from over 3,000 people selected by its 56 nodes around the world.